Determination of Four Pesticide Residues in Pepper Oleoresin and Pepper Essential Oil Using GPC-QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS and Dietary Risk Assessment
-
摘要:
本研究建立了胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油中甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯4种农药残留的凝胶渗透色谱-QuEChERS-气相色谱-串联质谱(GPC-QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS)检测方法。采用乙酸乙酯-环己烷溶液(1:1,V/V)提取,使用凝胶色谱仪结合石墨化碳黑吸附剂(GCB)、N-丙基乙二胺固相吸附剂(PSA)进行净化,多反应监测(MRM)模式检测,基质匹配标准曲线内标法定量分析。在优化的条件下,4种农药在3~100 μg/L浓度范围内的线性关系良好,相关系数均大于0.99,方法检出限为0.04~0.10 mg/kg,3个不同加标水平下的回收率均在73%~120%之间,相对标准偏差(RSD)均小于20%。收集市场上的胡椒、胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂各20批次,采用本方法检测样品中甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的最高残留量分别为1.236、0.954、2.087、1.174 mg/kg。基于实际样品中农药残留中位值,评估了胡椒、胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂中4种农药的慢性膳食摄入风险,结果远小于100%,表明其中的农药残留慢性摄入风险较小。
-
关键词:
- 胡椒油树脂 /
- 胡椒精油 /
- 农药残留 /
- 气相色谱-串联质谱(GC-MS/MS) /
- 慢性膳食摄入风险
Abstract:Pepper (Piper nigrum L.), a vital spice, is abundant in flavor compounds such as piperine, sesquiterpenes, and terpenes. Pepper oleoresin and pepper essential oil are concentrated extracts of these flavor compounds, can offer enhanced culinary value. Both oleoresin and essential oils contain numerous organic compounds, including volatile oils, organic acids, alkaloids, and pigments, posing challenges in detecting pesticide residues in these products. This study introduced a method of gel permeation chromatography combined with QuEChERS gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (GPC-QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS) to detect pesticide residues in pepper oleoresin and essential oil, incorporating dietary risk assessment. The extraction of the pesticde was conducted using an ethyl acetate-cyclohexane (1:1, V/V) solvent system, followed by gel permeation chromatography and purification with graphitized carbon black (GCB) and N-propyl ethylenediamine (PSA) adsorbents. The multi-reaction monitoring (MRM) mode and matrix-matched calibration curves with internal standards were used for quantitative analysis. Under optimized conditions, the four pesticides have good linearity in the concentration of 3-100 μg/L with the correlation coefficients exceeding 0.99. Recoveries at three spiked levels (0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mg/kg) range from 73% to 120%, suggesting high accuracy, and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) are below 20%, demonstrating good precision. The limits of detection are 0.04-0.10 mg/kg. A survey of 20 batches of black pepper, pepper essential oil, and pepper oleoresin on the market reveals maximum residue levels of metalaxyl, chlorpyrifos, permethrin, and cypermethrin at 1.236, 0.954, 2.087, and 1.174 mg/kg, respectively. A dietary risk assessment was conducted based on the median residue values determined in the samples. The results showed that the chronic dietary intake risks for four pesticides are significantly lower than 100%, indicating minimal dietary risks. This study not only provides a reliable and sensitive method for detecting pesticide residues in pepper extracts, but also contributes to establish food safety standards for plant-based extracts. Furthermore, it can offer valuable insights for internal quality control in the food processing industry and help regulatory bodies in enforcing food safety regulation.
-
胡椒(Piper nigrum L.)是一种重要的热带香辛料产物,全球年产量约44万吨,主要集中分布在越南、印度尼西亚、印度、巴西、斯里兰卡等国家,我国的胡椒产量约占全球的4.2%。海关统计数据显示[1-2],2023年我国胡椒进出口1.3万吨,贸易总额达4.4亿元。胡椒油树脂和胡椒精油是从胡椒中提取出来的,包含胡椒碱、胡椒脂碱、胡椒新碱以及倍半萜类和萜烯类化合物等风味物质[3-6],可直接替代胡椒粉添加至食品中[6],是重要的出口调味品。欧盟、美国等国家和地区已经颁布了胡椒或胡椒提取物的农药残留限量标准[7-10]。
目前,关于胡椒原料中痕量农药残留检测的报道较多[11-17]。吴南村等[11-12]使用QuEChERS-超高压液相色谱-串联质谱法检测胡椒中6种农药残留后,进一步使用分散固相萃取结合气相色谱-串联质谱法检测胡椒中19种农药残留。Yao等[13]使用QuEChERS提取,d-SPE净化结合高压液相色谱-串联质谱法测定胡椒中34种农药。Goon等[14]采用QuEChERS提取,HLB柱净化结合超高压离子阱-液相色谱-质谱法对胡椒中199种农药进行筛查和定量分析。Kandaswamy等[15]使用QuEChERS提取后,以N-丙基乙二胺固相吸附剂、石墨化碳等材料净化,结合超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法筛查和定量分析胡椒中133种农药。但是,关于胡椒提取物中农药残留的研究则较少。胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油是对胡椒原料进行提取加工的产物,其中含有大量的挥发油、有机酸、生物碱和色素等化合物[3-4],对农药残留检测过程的干扰较大,易产生较强的基质效应。
甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯是胡椒种植中允许使用的农药。本研究通过优化胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油等提取物的前处理方式,采用凝胶渗透色谱-QuEChERS-气相色谱-串联质谱(GPC-QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS)法测定胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油中4种农药残留,并评估胡椒提取物中甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的慢性膳食摄入风险,旨为胡椒提取物中多种农药残留检测提供技术支持。
1. 实验部分
1.1 仪器
7000B气相色谱-质谱联用仪:美国安捷伦科技有限公司产品;H-2050R高速冷冻离心机:湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司产品;SCI-RM涡旋混合器:美国Scientific Industries公司产品;BSA224S电子天平:德国Sartorius公司产品;凝胶渗透色谱仪:德国LC-Tech公司产品;DZKW-D-2电热恒温水浴锅:北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司产品;IKA RV10旋转蒸发仪:德国IKA公司产品。
1.2 材料与试剂
丙酮、正己烷:色谱级,美国Fisher公司产品;环己烷、乙酸乙酯、石墨化碳黑(GCB)、N-丙基乙二胺固相(PSA)吸附剂:上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司产品;氯氰菊酯、氯菊酯、毒死蜱、甲霜灵、环氧七氯:天津阿尔塔科技公司产品;有机滤膜(0.44、0.22 μm):天津艾杰尔公司产品。
1.3 实验条件
1.3.1 色谱条件
HP-5MS色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);不分流进样;进样量1.0 μL;进样口温度280 ℃;升温程序:初始温度50 ℃,保持1 min,以20 ℃/min升至130 ℃,再以10 ℃/min升至175 ℃,以5 ℃/min升至240 ℃,保持2 min,然后以20 ℃/min升至290 ℃,保持10 min;载气:高纯氦气(纯度>99.999%),流速 1 mL/min。
1.3.2 质谱条件
电子电离(EI)源,离子源温度230 ℃,四极杆温度150 ℃,传输线温度280 ℃,溶剂延迟13 min,碰撞气为氮气(纯度>99.999%),多反应监测(MRM)模式扫描。
1.3.3 凝胶色谱条件
净化柱:500 mm×25 mm,常规填料;流动相:乙酸乙酯-环己烷(1:1,V/V);流速5.0 mL/min;样品定量环5.0 mL;预淋洗体积135 mL(27 min);洗脱体积70 mL(14 min);清洗体积25 mL(5 min)。
1.4 样品前处理
将胡椒原料粉碎,过20目筛,充分混合均匀后称样;将胡椒油树脂经80 ℃加热后,充分摇匀,称样;胡椒精油直接称样。
分别称取2.5 g(精确至0.000 1 g)上述样品,依次加入5 mL乙酸乙酯、5 mL环己烷、200 μL内标工作液,置于涡旋混合器(2 500 r/min)涡旋混合3 min后,超声10 min,充分溶解,然后以10 000 r/min离心5 min,移取上清液,过0.44 μm尼龙滤膜,收集滤液至凝胶色谱仪;收集GPC淋洗液,水浴真空旋干,加入20 mL丙酮复溶,移取2 mL复溶液,添加至200 mg GCB+400 mg PSA,置于涡旋混合器(1 800 r/min)涡旋混合3 min后,以4 000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,过0.22 μm尼龙滤膜,收集滤液,待上机测试。
1.5 溶液配制
标准储备溶液配制:分别量取各100 μL氯氰菊酯、氯菊酯、毒死蜱、甲霜灵标准溶液(1 000 mg/L),用乙腈定容至25 mL,配制成4 mg/L混合标准工作溶液,−20 ℃密封保存,备用。
内标工作溶液配制:量取25 μL环氧七氯标准溶液(100 mg/L),用乙腈定容至25 mL,配制成0.1 mg/L内标工作溶液,−20 ℃密封保存,备用。
基质标准工作溶液配制:使用未检出上述4种农药的样品作为空白,按1.4节方法处理样品,得到空白基质溶液,用空白基质溶液稀释混合标准储备液,分别配制成100、50、25、12、6、3 μg/L系列浓度的基质标准工作溶液,现用现配。
1.6 基质效应
胡椒提取物中的内源性或外源性物质会影响分析物的离子化效率,使目标物的质谱响应增加或降低,从而产生基质效应(matrix effect, ME),对分析准确性产生较大影响[16-18]。参考生姜提取物的基质效应评价方法进行评估[19],计算公式如下:
ME=(基质匹配标准曲线的斜率溶剂标准曲线的斜率−1)×100% (1) |ME|<20%为弱基质效应;20%≤|ME|≤50%为中等基质效应;|ME|>50%为强基质效应。当|ME|≥20%时,需使用基质标准曲线作为回归方程,使用校准后的曲线进行计算以消除基质效应的影响[20-21]。
1.7 慢性膳食摄入风险评估
依照农药毒理学数据对人体摄入膳食量进行慢性膳食风险评估(%ADI)[18,22],甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的ADI数值从《GB 2763−2021 食品安全国家标准 食品中农药最大残留限量》[23]中获取,胡椒油树脂和胡椒精油的每日膳食摄入量采取最大风险值,公式如下:
NEDI=STMR×Fb.w. (2) %ADI=NEDIADI×100 (3) 式中:NEDI为国家估算每日摄入量(mg/kg·b.w.);STMR为农药残留中位值(mg/kg);F为胡椒油树脂或胡椒精油摄入量,按酱油类计算[19,24];b.w.为我国的平均体重,参照《第五次国民体质监测公报》平均体重[25];ADI为每日允许摄入量(mg/kg·b.w.)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 色谱条件优化
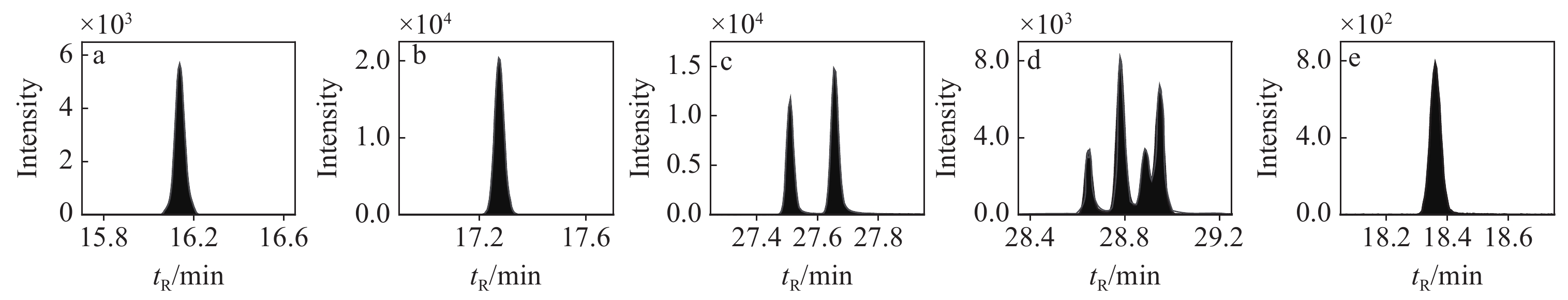
首先配制质量浓度为1 mg/kg的甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯、环氧七氯5种化合物混合对照溶液,通过全扫描模式确定各目标化合物的保留时间和质谱图,然后在MRM模式下对目标化合物的母离子、子离子及碰撞能量进行优化,获取质谱参数,并根据峰面积和信噪比确定每种化合物的定性和定量离子,建立质谱检测方法。4种农药及内标的定性、定量离子列于表1,MRM谱图示于图1。
表 1 5种化合物的最佳质谱参数Table 1. Optimal mass spectrometry parameters of five compound pesticides序号
No.化合物
Compound保留时间
Retention time/
min定量离子
Quantitative ion
(m/z)碰撞能量
Cone voltage/
eV定性离子
Qualitative ion
(m/z)碰撞能量
Cone voltage/
eV1 甲霜灵 Metalaxyl 16.18 249>146 20 160>130 20 2 毒死蜱 Chlorpyrifos 17.27 314>258 14 197>169 15 3 氯菊酯 Permethrin 27.52, 27.68 163>127 5 183>153 15 4 氯氰菊酯 Cypermethrin 28.60, 29.0 163>127 5 181>152 25 5 环氧七氯 Heptachlor epoxide(内标) 18.38 354.8>264.9 15 352.8>262.9 15 2.2 样品前处理优化
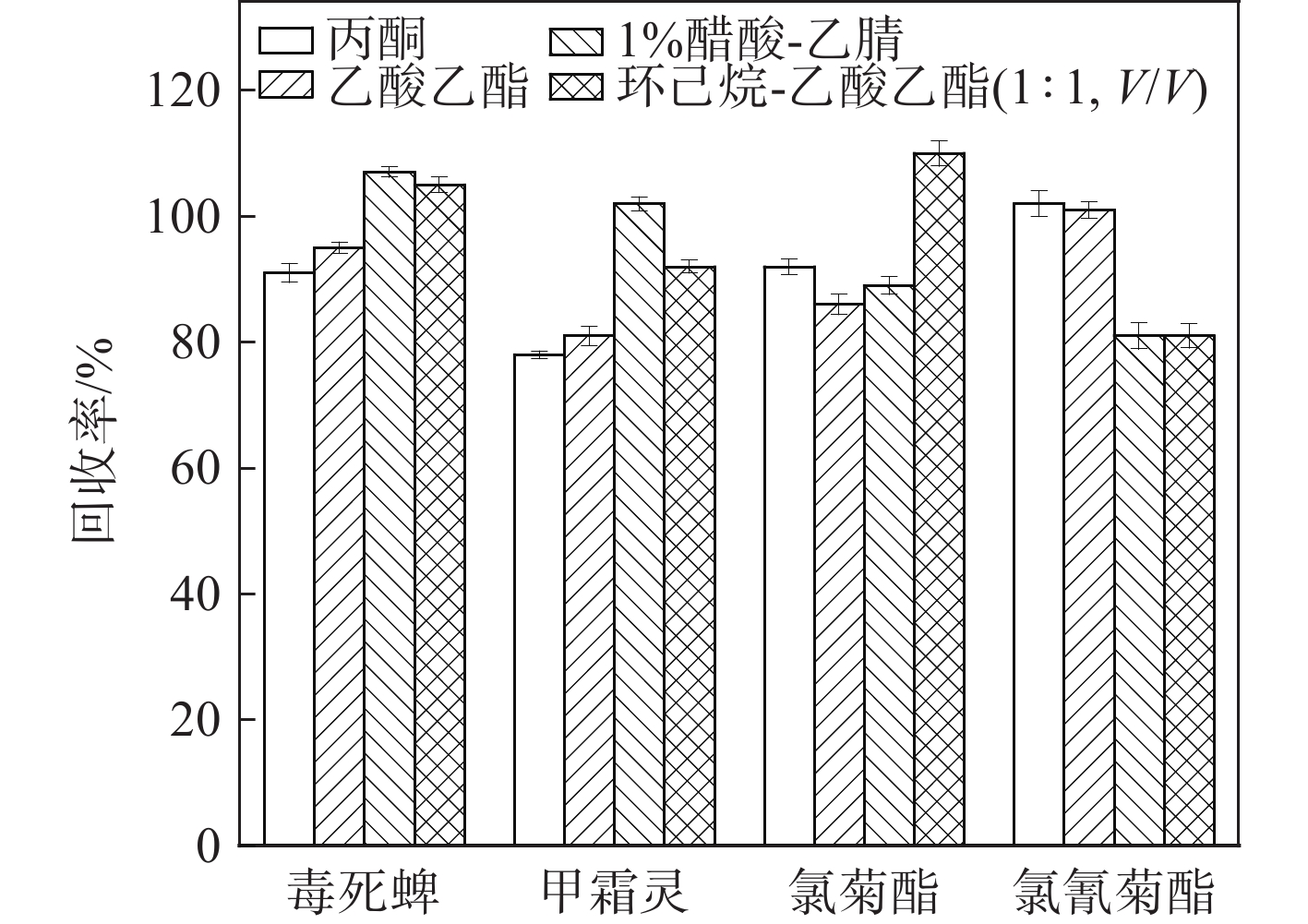
选择合适的提取溶剂和净化方式对后续的检测尤为重要[26-29]。本实验考察了丙酮、乙酸乙酯、1%醋酸-乙腈、环己烷-乙酸乙酯(1:1,V/V)等提取溶剂对胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂中农药的提取效果,结果示于图2。可见,4种提取溶剂的加标回收率在78%~110%之间,均能较好地提取样品中的农药。若使用其他溶剂,在使用凝胶色谱净化胡椒提取物时,需要对提取溶剂旋蒸干燥后,再使用凝胶色谱流动相(环己烷-乙酸乙酯(1:1,V/V))复溶上机,置换溶剂,容易造成目标化合物损失,且检测结果精密度较差。因此,选择环己烷-乙酸乙酯(1:1,V/V)作为提取溶剂,丙酮作为复溶溶剂。
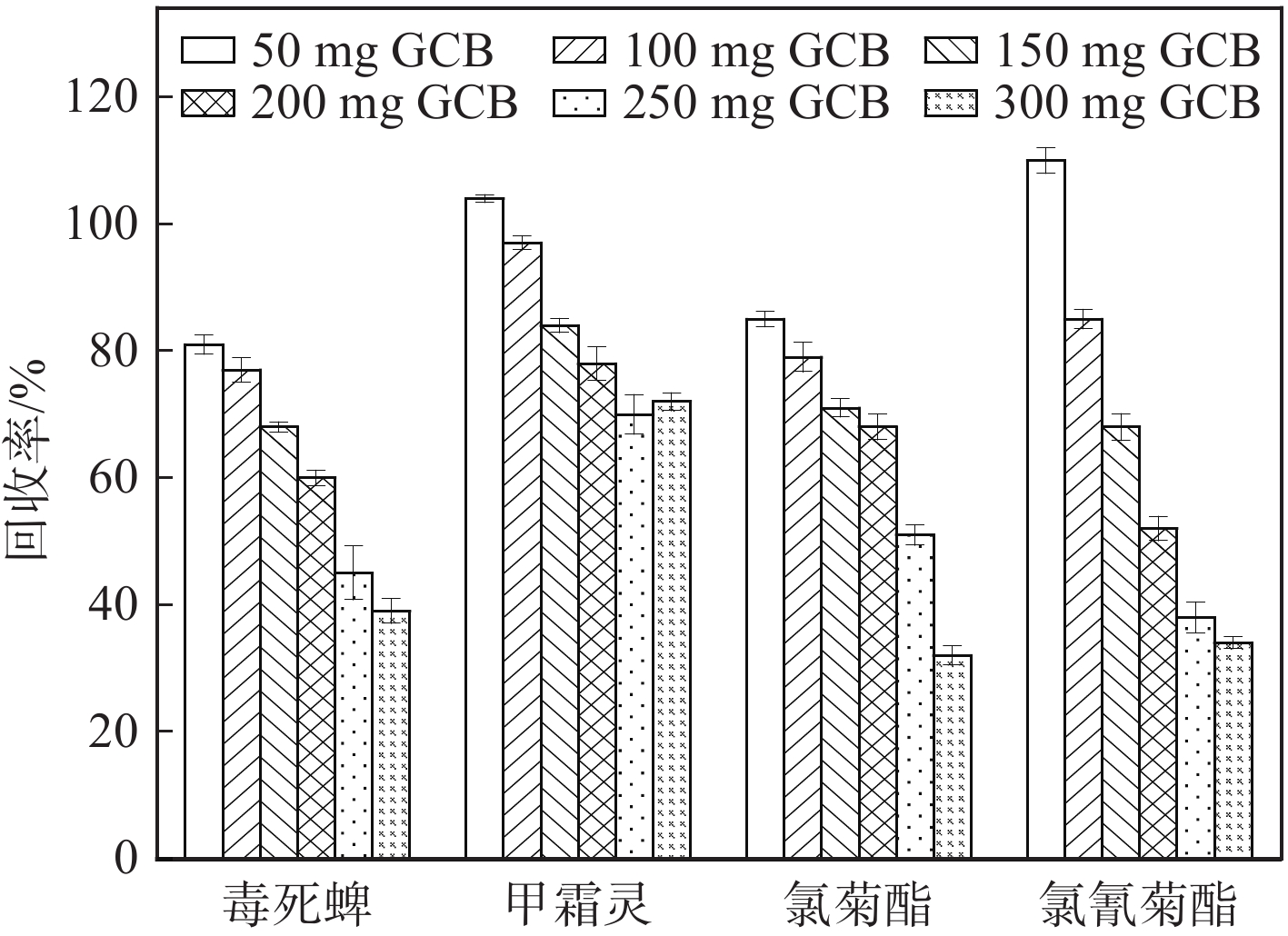
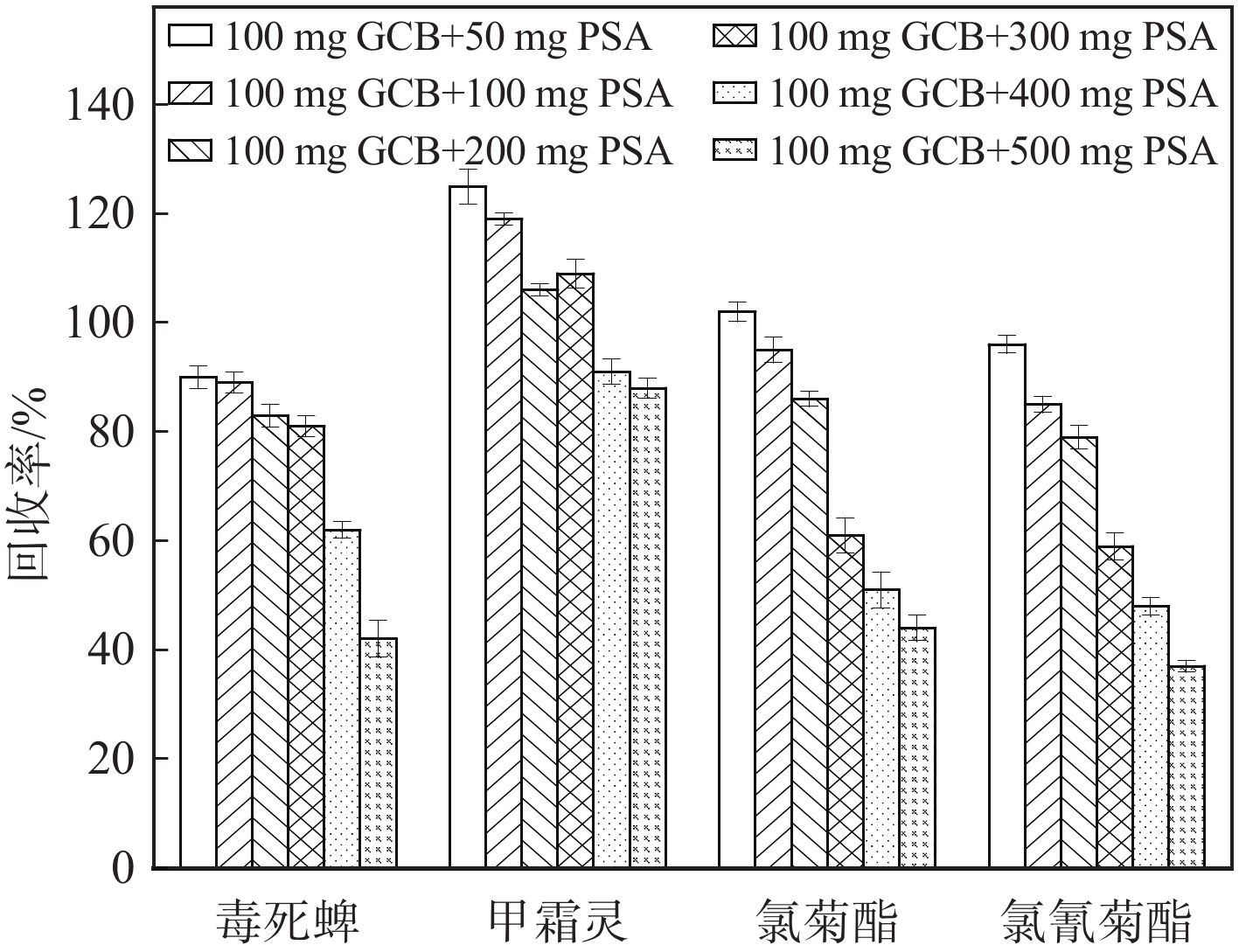
胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂是胡椒原料经干燥、粉碎、萃取、浓缩后的产物,含有色素、有机酸、胡椒碱、挥发油等成分,基质较为复杂[3-6],如果直接净化,耗费材料多且易污染仪器。使用GPC去除部分油脂、色素等大分子物质后,再结合QuEChERS进一步净化[28-29]。PSA、GCB能够吸附有机酸、色素等物质[29],但用量较多可能会吸附目标化合物,用量较少则净化不完全,因此,需要考察PSA、GCB的添加量。本实验取1 mL复溶液,分别添加50、100、150、200、250、300 mg GCB考察净化效果,结果示于图3。可见,随着GCB添加量的增加,4种农药的回收率逐渐降低,考虑GCB对回收率的影响,选择100 mg GCB进行净化,但净化后复溶液颜色较深,表明还存在色素。因此,在1 mL复溶液中添加100 mg GCB的基础上,再分别添加50、100、200、300、400、500 mg PSA考察净化效果,结果示于图4。可见,随着PSA添加量的增加,4种农药的回收率逐渐降低。综合考虑,选择100 mg GCB+200 mg PSA进行净化。
2.3 基质效应评价
基质种类、基质数量和目标化合物化学性质对基质效应有一定的影响[20]。胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油中的挥发油、有机酸、生物碱和色素等杂质易引起基质增强或抑制效应,其评价结果列于表2,4种农药的基质效应在20%~90%之间,多为基质增强效应。
表 2 4种目标化合物的标准曲线、基质效应、检出限和定量限Table 2. Linear equations, matrix effect, limits of detection (LODs) and limits of quantification (LOQs) of four target compounds化合物
Compound样品基质
Sample matrix线性方程
Linear equation相关系数
Correlation coefficient (R2)基质效应
Matrix effect/%检出限
LOD/(mg/kg)定量限
LOQ/(mg/kg)甲霜灵 胡椒 y=1.8142x−0.0807 0.9946 22 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=2.9298x−0.0411 0.9988 97 0.05 0.15 胡椒油树脂 y=1.9025x−0.0522 0.9992 28 0.05 0.15 毒死蜱 胡椒 y=4.9932x−0.0734 0.9991 20 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=5.6550x+0.2560 0.9987 35 0.05 0.15 胡椒油树脂 y=5.0965x+0.1422 0.9990 23 0.05 0.15 氯菊酯 胡椒 y=10.3357x−0.0783 0.9989 33 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=14.5634x+0.6831 0.9990 90 0.10 0.30 胡椒油树脂 y=12.0358x−0.0948 0.9981 57 0.10 0.30 氯氰菊酯 胡椒 y=9.1492x−0.2560 0.9945 27 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=10.3133x−0.3316 0.9997 44 0.05 0.15 胡椒油树脂 y=9.3747x−0.2239 0.9975 31 0.05 0.15 2.4 线性范围、检出限和定量限
本实验采用基质标准曲线内标法进行定量分析,以环氧七氯作为内标,目标化合物和内标的浓度比为横坐标,响应面积比为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,结果列于表2。可见,4种农药在3~200 μg/L浓度范围内的线性关系良好,相关系数(R2)在0.994 5~0.999 7之间,以3倍和10倍信噪比分别确定方法的检出限(LOD)和定量限(LOQ)为0.04~0.10、0.12~0.30 mg/kg。
2.5 加标回收率及精密度
本实验选择农药残留较低的胡椒、胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂样品,分别添加0.1、0.5、1.0 mg/kg 3个浓度水平的4种农药,每个浓度水平做6次平行实验,考察方法回收率和精密度,结果列于表3。可见,平均回收率在73%~120%之间,相对标准偏差(RSD)小于20%,符合《GB27404实验室质量控制规范 食品理化检测》[30]的要求。
表 3 不同加标水平下4种农药的回收率及相对标准偏差(n=6)Table 3. Average recoveries and relative standard deviations (RSDs) of four pesticides at different spiking levels (n=6)化合物
Compound添加水平
Spiked/
(mg/kg)胡椒
Pepper胡椒精油
Pepper essential oil胡椒油树脂
Pepper oleoresin回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%甲霜灵 0.1 110 8 78 17 89 15 0.5 101 15 89 11 95 16 1.0 97 14 91 10 99 11 毒死蜱 0.1 80 10 77 9 75 9 0.5 79 11 80 14 86 5 1.0 73 18 86 15 80 12 氯菊酯 0.1 75 7 72 19 77 15 0.5 80 9 75 8 82 16 1.0 89 8 83 12 92 9 氯氰菊酯 0.1 109 16 120 13 105 12 0.5 105 13 118 19 109 8 1.0 115 17 109 15 98 6 2.6 实际样品检测
利用该方法测定市售的20份胡椒、20份胡椒油树脂和20份胡椒精油样品,结果列于表4。胡椒油树脂中,甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯阳性样品的检出率分别为60%、55%、35%、75%;胡椒精油中阳性样品的检出率分别为45%、40%、70%、65%;胡椒提取物农药检出率高于胡椒原料。胡椒提取物中,甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的最高残留量分别为1.236、0.954、2.087、1.174 mg/kg,明显高于胡椒原料,表明在胡椒加工过程中,农药随胡椒提取物一起被浓缩富集。鉴于目前各国家和组织尚未明确规定胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油产品中农药的最高残留限量(MRL)标准,建议根据农药的ADI、提取物原料的MRL,并结合提取浓缩情况,制定各类植物提取物的MRL标准。
表 4 市售样品中4种农药残留检测Table 4. Detection of four pesticide residues in commercial samples化合物
Compound胡椒 Pepper 胡椒精油 Pepper essential oil 胡椒油树脂 Pepper oleoresin 农药残留
Pesticide residue/
(mg/kg)检出率
Rate of positive sample/%农药残留
Pesticide residue/
(mg/kg)检出率
Rate of positive sample/%农药残留
Pesticide residue/
(mg/kg)检出率
Rate of positive sample/%甲霜灵 <0.020~0.098 15 <0.050~1.236 60 <0.050~0.908 45 毒死蜱 <0.008~0.083 10 <0.050~0.479 55 <0.050~0.954 40 氯菊酯 <0.040~0.119 10 <0.100~0.610 35 <0.100~2.087 70 氯氰菊酯 <0.020~0.194 25 <0.050~1.174 75 <0.050~1.163 65 2.7 慢性膳食风险评估
《GB 2763−2021食品安全国家标准 食品中农药最大残留限量》[23]中规定,甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的ADI分别为0.08、0.01、0.05、0.02 mg/kg·b.w.,基于实际样品中农药残留中位值,计算得到胡椒油树脂、胡椒精油中甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的慢性膳食摄入风险,结果列于表5。4种农药的慢性膳食风险评估结果在0.01%~0.71%之间,慢性摄入风险远小于100%,表明胡椒油树脂和胡椒精油中农药残留的慢性摄入风险较小。
表 5 4种农药慢性膳食摄入风险评估计算表Table 5. Calculation table for risk assessment of chronic dietary intake of four pesticides样品
Sample膳食量
Dietary amount/g甲霜灵
Carbendazim
(ADI:0.08 mg/kg·b.w.)毒死蜱
Chlorpyrifos
(ADI:0.01 mg/kg·b.w.)氯菊酯
Permethrin
(ADI:0.05 mg/kg·b.w.)氯氰菊酯
Cypermethrin
(ADI:0.02 mg/kg·b.w.)农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险
ADI/%农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险ADI/% 农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险ADI/% 农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险ADI/% 胡椒 9.00 0.038 0.01 0.040 0.06 0.081 0.02 0.067 0.05 胡椒
精油9.00 0.419 0.07 0.113 0.16 0.317 0.09 0.503 0.36 胡椒油树脂 9.00 0.312 0.06 0.495 0.71 0.833 0.24 0.477 0.34 3. 结论
本研究建立了GPC-QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS法测定胡椒、胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂中4种农药残留。在3~100 μg/L浓度范围内,4种农药的线性关系良好,相关系数均大于0.99,方法检出限为0.04~0.10 mg/kg,3个不同加标水平的回收率在73%~120%之间,相对标准偏差(RSD)均小于20%。该方法净化效果好、灵敏度高,可应用于市售胡椒、胡椒精油、胡椒油树脂中农药残留的检测。基于实际检测样品农药残留中位值,评估胡椒、胡椒精油和胡椒油树脂中甲霜灵、毒死蜱、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯的慢性膳食摄入风险,胡椒油树脂和胡椒精油中农药残留的慢性膳食暴露风险较小。
-
表 1 5种化合物的最佳质谱参数
Table 1 Optimal mass spectrometry parameters of five compound pesticides
序号
No.化合物
Compound保留时间
Retention time/
min定量离子
Quantitative ion
(m/z)碰撞能量
Cone voltage/
eV定性离子
Qualitative ion
(m/z)碰撞能量
Cone voltage/
eV1 甲霜灵 Metalaxyl 16.18 249>146 20 160>130 20 2 毒死蜱 Chlorpyrifos 17.27 314>258 14 197>169 15 3 氯菊酯 Permethrin 27.52, 27.68 163>127 5 183>153 15 4 氯氰菊酯 Cypermethrin 28.60, 29.0 163>127 5 181>152 25 5 环氧七氯 Heptachlor epoxide(内标) 18.38 354.8>264.9 15 352.8>262.9 15 表 2 4种目标化合物的标准曲线、基质效应、检出限和定量限
Table 2 Linear equations, matrix effect, limits of detection (LODs) and limits of quantification (LOQs) of four target compounds
化合物
Compound样品基质
Sample matrix线性方程
Linear equation相关系数
Correlation coefficient (R2)基质效应
Matrix effect/%检出限
LOD/(mg/kg)定量限
LOQ/(mg/kg)甲霜灵 胡椒 y=1.8142x−0.0807 0.9946 22 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=2.9298x−0.0411 0.9988 97 0.05 0.15 胡椒油树脂 y=1.9025x−0.0522 0.9992 28 0.05 0.15 毒死蜱 胡椒 y=4.9932x−0.0734 0.9991 20 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=5.6550x+0.2560 0.9987 35 0.05 0.15 胡椒油树脂 y=5.0965x+0.1422 0.9990 23 0.05 0.15 氯菊酯 胡椒 y=10.3357x−0.0783 0.9989 33 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=14.5634x+0.6831 0.9990 90 0.10 0.30 胡椒油树脂 y=12.0358x−0.0948 0.9981 57 0.10 0.30 氯氰菊酯 胡椒 y=9.1492x−0.2560 0.9945 27 0.04 0.12 胡椒精油 y=10.3133x−0.3316 0.9997 44 0.05 0.15 胡椒油树脂 y=9.3747x−0.2239 0.9975 31 0.05 0.15 表 3 不同加标水平下4种农药的回收率及相对标准偏差(n=6)
Table 3 Average recoveries and relative standard deviations (RSDs) of four pesticides at different spiking levels (n=6)
化合物
Compound添加水平
Spiked/
(mg/kg)胡椒
Pepper胡椒精油
Pepper essential oil胡椒油树脂
Pepper oleoresin回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%甲霜灵 0.1 110 8 78 17 89 15 0.5 101 15 89 11 95 16 1.0 97 14 91 10 99 11 毒死蜱 0.1 80 10 77 9 75 9 0.5 79 11 80 14 86 5 1.0 73 18 86 15 80 12 氯菊酯 0.1 75 7 72 19 77 15 0.5 80 9 75 8 82 16 1.0 89 8 83 12 92 9 氯氰菊酯 0.1 109 16 120 13 105 12 0.5 105 13 118 19 109 8 1.0 115 17 109 15 98 6 表 4 市售样品中4种农药残留检测
Table 4 Detection of four pesticide residues in commercial samples
化合物
Compound胡椒 Pepper 胡椒精油 Pepper essential oil 胡椒油树脂 Pepper oleoresin 农药残留
Pesticide residue/
(mg/kg)检出率
Rate of positive sample/%农药残留
Pesticide residue/
(mg/kg)检出率
Rate of positive sample/%农药残留
Pesticide residue/
(mg/kg)检出率
Rate of positive sample/%甲霜灵 <0.020~0.098 15 <0.050~1.236 60 <0.050~0.908 45 毒死蜱 <0.008~0.083 10 <0.050~0.479 55 <0.050~0.954 40 氯菊酯 <0.040~0.119 10 <0.100~0.610 35 <0.100~2.087 70 氯氰菊酯 <0.020~0.194 25 <0.050~1.174 75 <0.050~1.163 65 表 5 4种农药慢性膳食摄入风险评估计算表
Table 5 Calculation table for risk assessment of chronic dietary intake of four pesticides
样品
Sample膳食量
Dietary amount/g甲霜灵
Carbendazim
(ADI:0.08 mg/kg·b.w.)毒死蜱
Chlorpyrifos
(ADI:0.01 mg/kg·b.w.)氯菊酯
Permethrin
(ADI:0.05 mg/kg·b.w.)氯氰菊酯
Cypermethrin
(ADI:0.02 mg/kg·b.w.)农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险
ADI/%农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险ADI/% 农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险ADI/% 农药残留中位数
Median pesticide residue/(mg/kg)慢性膳食风险ADI/% 胡椒 9.00 0.038 0.01 0.040 0.06 0.081 0.02 0.067 0.05 胡椒
精油9.00 0.419 0.07 0.113 0.16 0.317 0.09 0.503 0.36 胡椒油树脂 9.00 0.312 0.06 0.495 0.71 0.833 0.24 0.477 0.34 -
[1] 刘红, 谭乐和, 邬华松, 谷风林, 初众, 宗迎, 朱红英, 魏来. 青胡椒油树脂化学成分的研究[J]. 农学学报, 2013, 3(2): 70 -74 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7774.2013.02.015LIU Hong, TAN Lehe, WU Huasong, GU Fenglin, CHU Zhong, ZONG Ying, ZHU Hongying, WEI Lai. The analysis of chemical constituents of green pepper oleoresin[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2013, 3(2):
70 -74 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7774.2013.02.015[2] 曾小红, 李光辉, 王小芳, 胡杰. 中国胡椒生产和贸易发展分析[J]. 热带农业科学, 2023, 43(9): 108 -113 .ZENG Xiaohong, LI Guanghui, WANG Xiaofang, HU Jie. An analysis of pepper production and trade situation in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2023, 43(9):
108 -113 (in Chinese).[3] 蒋云聪, 魏占姣, 张晶晶, 刘英雪, 齐立军. 胡椒油树脂精制工艺研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2021, 32(4): 46 -49 .JIANG Yuncong, WEI Zhanjiao, ZHANG Jingjing, LIU Yingxue, QI Lijun. Research on refining process of black pepper oleoresin[J]. China Food Additives, 2021, 32(4):
46 -49 (in Chinese).[4] 景正义, 张玉涵, 蒋云聪, 魏占姣, 张玉婷, 李腾飞. 胡椒精油不同馏分化学成分及风味分析[J]. 中国调味品, 2023, 48(1): 175 -180 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.01.032JING Zhengyi, ZHANG Yuhan, JIANG Yuncong, WEI Zhanjiao, ZHANG Yuting, LI Tengfei. Chemical components and flavor analysis of different distillates of pepper essential oil[J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(1):
175 -180 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.01.032[5] 景正义. 胡椒精油挥发性风味物质分析与应用研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2023. [6] 陈星星, 宋丽, 谷风林, 吴桂苹, 陶锐. 三相分离法提取胡椒油树脂的工艺研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2020, 41(8): 1 674-1 682. CHEN Xingxing, SONG Li, GU Fenglin, WU Guiping, TAO Rui. Processing parameters of extracting pepper oleoresin by three phase partitioning[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2020, 41(8): 1 674-1 682(in Chinese).
[7] Bryant Christie Inc.2018. MRL datanase[EB/OL]. (2024-03-11) [2024-05-30]. http://www.mrldatabase.com/.
[8] Codes Alimentarius. 2019. International food standards initiative[EB/OL]. (2019-11-04) [2024-05-30]. http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/standads/pestres/pesticides/zh/.
[9] Government of Canada. 2019. MRL database[EB/OL]. (2024-03-19) [2024-05-30]. http://pr-rp.hc-sc.gc.ca/mrl-lrm/rseults-eng.php.
[10] European Commission. 2017. Pesticides Web Version-EU MRLs[EB/OL]. (2024-02-18)[2024-05-30]. http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eupesticides-database/public/?event=pesticide.residue.CurrentMRL&language=EN&pestResidueld=188.
[11] 吴南村, 刘春华, 乐渊, 张群, 陈井清. QuEChERS-超高压液相色谱-串联质谱法检测黑胡椒中6种农药残留[J]. 分析试验室, 2018, 37(12): 1 431-1 435. WU Nancun, LIU Chunhua, LE Yuan, ZHANG Qun, CHEN Jingqing. Simultaneous determination of black pepper using QuEChERS-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2018, 37(12): 1 431-1 435(in Chinese).
[12] 吴南村, 张群, 李春丽, 刘春华, 乐渊, 吴学进. 分散固相萃取结合气相串联质谱法检测黑胡椒中19种农药残留[J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(3): 656 -661 .WU Nancun, ZHANG Qun, LI Chunli, LIU Chunhua, LE Yuan, WU Xuejin. Determination of 19 pesticides residue in black pepper using dispersive solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(3):
656 -661 (in Chinese).[13] YAO W, ZHANG Z, SONG S, HAO X, XU Y, HAN L. Multi-residue analysis of 34 pesticides in black pepper by QuEChERS with d-SPE vs. d-SLE cleanup[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2019, 12(1):
176 -189 . doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1350-7[14] GOON A, KHAN Z, OULKAR D, SHINDE R, GAIKWAD S, BANERJEE K. A simultaneous screening and quantitative method for the multiresidue analysis of pesticides in spices using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution (Orbitrap) mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2018, 1 532: 105-111.
[15] KANDASWAMY C, ANANDARAM S, DAVIS PRESLEY S I, SHABEER A T P. Comparative evaluation of multi-residue methods for analysis of pesticide residues in black pepper by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: critical evaluation of matrix co-extractives and method validation[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 58(3):
911 -920 . doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04605-0[16] 张金环, 朱欢, 李伟霞, 李桂红, 程艳宇. 农药残留检测中基质效应的研究进展[J]. 农药科学与管理, 2023, 44(4): 15 -18, 29 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2023.04.003ZHANG Jinhuan, ZHU Huan, LI Weixia, LI Guihong, CHENG Yanyu. Research progress of matrix effects in pesticide residue detection[J]. Pesticide Science and Administration, 2023, 44(4):
15 -18, 29 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2023.04.003[17] CHAMBERS E, WAGROWSKI-DIEHL D M, LU Z, MAZZEO J R. Systematic and comprehensive strategy for reducing matrix effects in LC/MS/MS analyses[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 2007, 852(1/2):
22 -34 .[18] ERNEY D R, GILLESPIE A M, GILVYDIS D M, POOLE C F. Explanation of the matrix-induced chromatographic response enhancement of organophosphorus pesticides during open tubular column gas chromatography with splitless or hot on-column injection and flame photometric detection[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 1993, 638(1):
57 -63 . doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(93)85007-T[19] 钱建瑞, 张玉芬, 李晓伟, 武亚明, 张学金, 吴迪. QuEChERS-LC-MS/MS测定姜油树脂、姜精油中8种农药残留及膳食风险评估[J]. 质谱学报, 2024, 45(2): 281-291. QIAN Jianrui, ZHANG Yufen, LI Xiaowei, WU Yaming, ZHANG Xuejin, WU Di. Determination and dietary risk assessment of 8 pesticide residues in ginger oleoresin and ginger essential Oil by QuEChERS-LC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2024, 45(2): 281-291(in Chinese).
[20] 黄宝勇, 欧阳喜辉, 潘灿平. 色谱法测定农产品中农药残留时的基质效应[J]. 农药学学报, 2005(4): 299 -305 . doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-7303.2005.04.002HUANG Baoyong, OUYANG Xihui, PAN Canping. Matrix effects in the analysis of pesticide residue in agro-products by chromatographic methods[J]. Chinese Jouranl of Pesticide Science, 2005(4):
299 -305 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-7303.2005.04.002[21] ZHANG Q, DUAN Y, MA C, TIAN H, HUAN Z, WU X. Determination of residual quantity from five pesticides and their metabolites in cowpea and dietary risk assessment[J]. China Vegetables, 2022, 404(10):
86 -96 .[22] 蒋玉艳, 赵鹏. 食品化学污染物膳食暴露风险评估研究进展[J]. 应用预防医学, 2019, 25(5): 432 -435 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-758X.2019.05.026JIANG Yuyan, ZHAO Peng. Research progress on dietary exposure risk assessment of food chemical pollutants[J]. Applied Prev Med, 2019, 25(5):
432 -435 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-758X.2019.05.026[23] GB 2763−2021. 食品安全国家标准 食品中农药最大残留限量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. [24] 孙健, 芦仙慧, 周孟, 冯义志, 潘金菊, 张爱娟, 马新刚, 梁林, 左伯军. 人参、三七、山药、百合和姜中甲霜灵和嘧菌酯残留分析及长期膳食风险评估[J]. 农药, 2023, 62(1): 36 -42, 66 .SUN Jian, LU Xianhui, ZHOU Meng, FENG Yizhi, PAN Jinju, ZHANG Aijuan, MA Xingang, LIANG Lin, ZUO Bojun. Residue analysis and long-term dietary risk assessment of metalaxyl and azoxystrobin in ginseng, pseudoginseng, yam, lily, and ginger[J]. Agrochemicals, 2023, 62(1):
36 -42, 66 (in Chinese).[25] General administration of sport of the people's republic of China. Bulletin of the fifth national physical fitness monitoring[EB/OL]. (2021-12-30)[2023-03-25]. http://www.gov.cn/guoqing/2023-03/12/content_5745851.htm.
[26] 李洁, 王艳丽, 李芳芳, 田其燕, 鞠香, 刘艳明. 改进的QuEChERS方法结合在线凝胶色谱-气相色谱-串联质谱技术测定植物油中74种农药残留[J]. 分析化学, 2023, 51(10): 1 693-1 702. LI Jie, WANG Yanli, LI Fangfang, TIAN Qiyan, JU Xiang, LIU Yanming. Determination of 74 kinds of pesticide residues in vegetable oil by improved QuEChERS method combined with on-line gel permeation chromatography-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(10): 1 693-1 702(in Chinese).
[27] 周建峰, 陈鑫兰, 颜艳阳, 李志梅, 朱海佩, 隋玉杰. GPC/SPE-UPLC-MS/MS凝胶色谱仪辅助分散型固相萃取-快速检测桃胶中10种杀虫剂和杀菌剂农药残留[J]. 中国测试, 2022, 48(S2): 108 -114 .ZHOU Jianfeng, CHEN Xinlan, YAN Yanyang, LI Zhimei, ZHU Haipei, SUI Yujie. GPC/SPE-UPLC-MS/MS-rapid determination from GPC and dispersed solid phase extraction of 10 insecticides and fungicides residues in peach gum[J]. China Measurement & Test, 2022, 48(S2):
108 -114 (in Chinese).[28] 李洁, 鞠香, 王艳丽, 田其燕, 梁秀清, 李海霞, 刘艳明. QuEChERS-在线凝胶渗透色谱-气相色谱-串联质谱法高通量筛查动物源性食品中的多农药残留[J]. 色谱, 2023, 41(7): 610 -621 . doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.10010LI Jie, JU Xiang, WANG Yanli, TIAN Qiyan, LIANG Xiuqing, LI Haixia, LIU Yanming. High-throughput screening of multi-pesticide residues in animal-derived foods by QuEChERS-online gel permeation chromatography-gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2023, 41(7):
610 -621 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.10010[29] 李自强, 杨梅, 张新忠, 罗逢健, 楼正云, 梁爽. 改良QuEChERS方法与UPLC-MS/MS联用测定茶叶中草甘膦、草铵膦及氨甲基膦酸[J]. 茶叶科学, 2023, 43(2): 263 -274 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2023.02.011LI Ziqiang, YANG Mei, ZHANG Xinzhong, LUO Fengjian, LOU Zhengyun, LIANG Shuang. Simultaneous determination of glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethyl phosphonic acid residues in tea by modified QuEChERS method coupled with UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2023, 43(2):
263 -274 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2023.02.011[30] GB/T 27404−2008. 实验室质量控制规范 食品理化检测[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.



 下载:
下载: